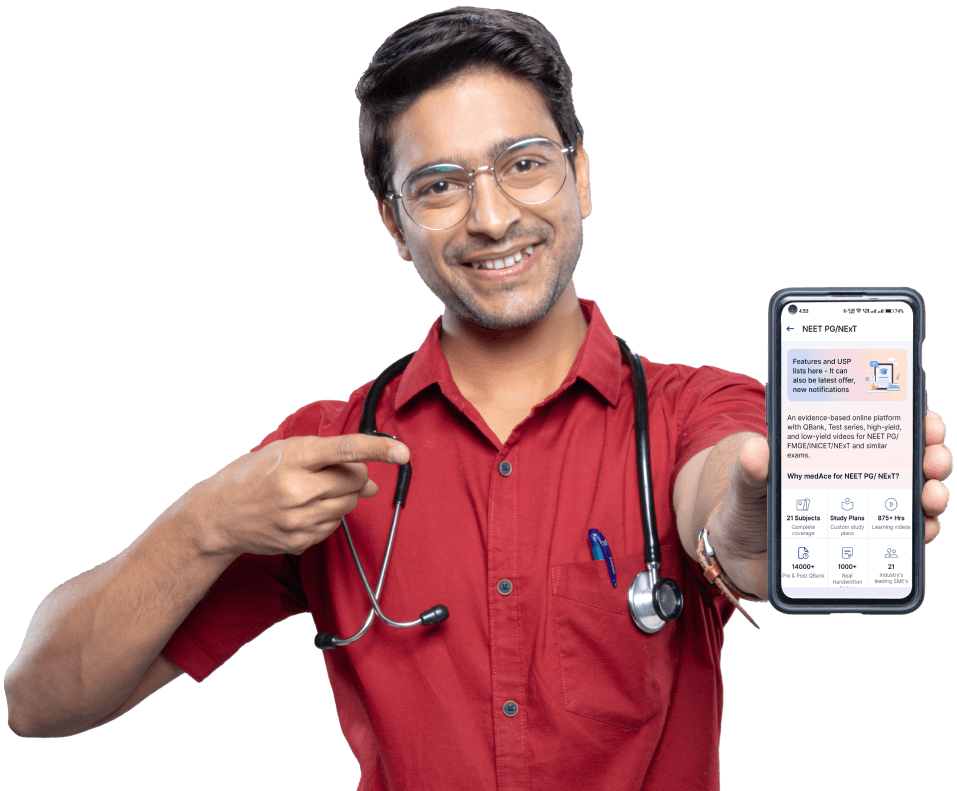
Basic Sciences for MBBS Students
Build a strong foundation with enriching learning videos, quick revisions and exam-focused tests


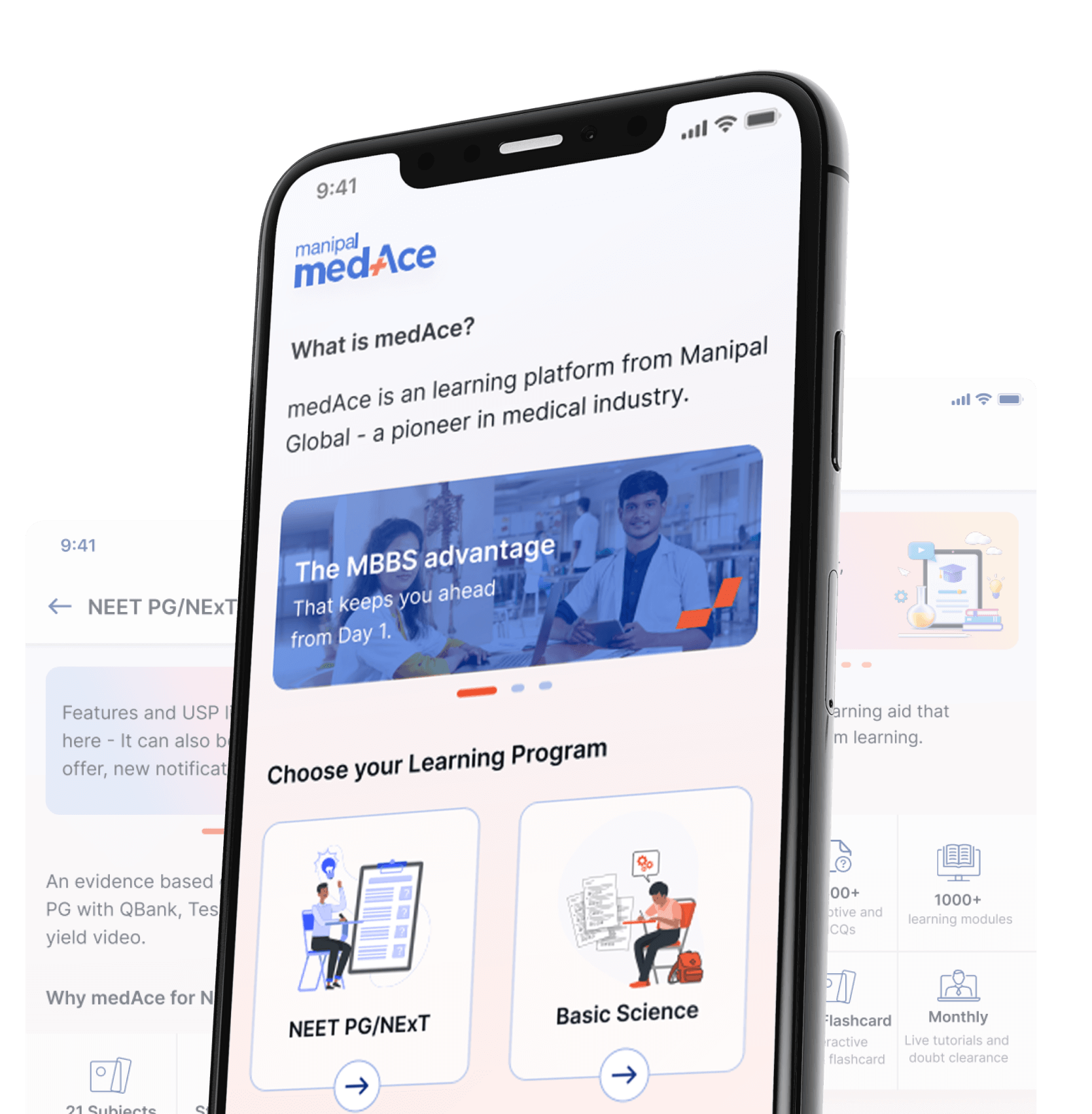
Program Overview
Start your MBBS journey by building a strong foundation and improving core medical knowledge with our Basic Sciences course. This course covers all fundamental principles underlying human biology, anatomy, physiology, biochemistry, pharmacology, pathology, microbiology, community medicine and more. This course is designed to equip aspiring doctors with the knowledge required to pursue a successful career in medicine.
Based on e-learning principles, this course includes immersive learning videos, live discussions and tests curated by India’s top
faculty to simplify complex concepts.
CBME
Mapped integrated curriculum
1500+
Descriptive and MCQs
1000+
Learning modules
2000+
Glossary for Quick Search
CYU / Flashcard
Interactive test & flashcard
Monthly
Live tutorials and doubt clearance
Benefits
Fact-Checked by Doctors
Rigorous quality check of all content at multiple stages by faculty and doctors themselves to ensure it is error-free

Interactive Flashcards
Use flashcards to quickly review each topic and enhance your understanding of key medical concepts
Dissection Videos
Broaden your understanding of the human anatomy with real-life dissection videos to take learning from classroom to clinic.
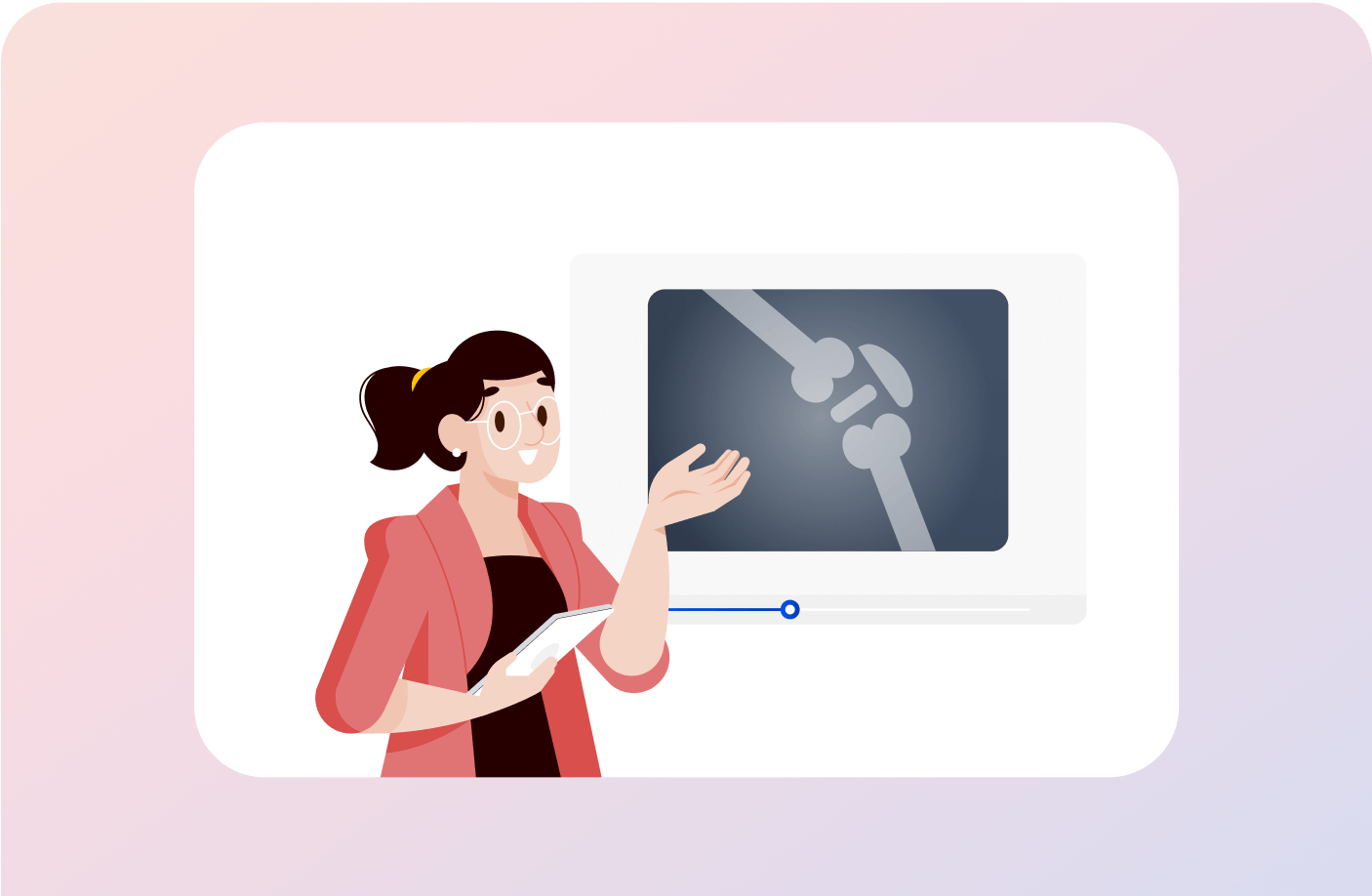
New-Age Immersive Videos
Interact with responsive videos that feature dynamic 3D models to make learning fun, easy and engaging.
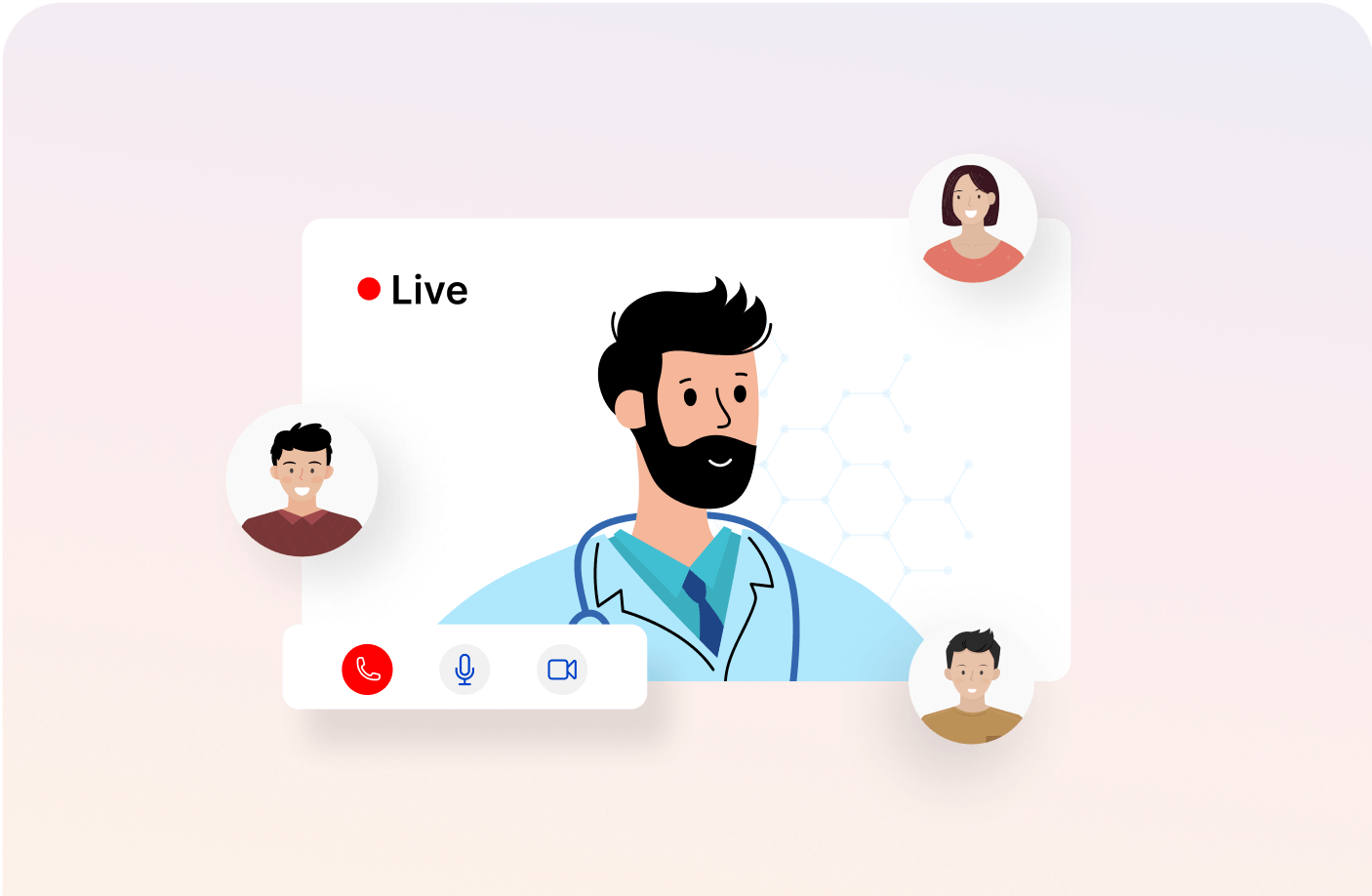
Real-time Mentoring Sessions
Get live tutoring for difficult topics and a chance to connect directly with peers and mentors to solve doubts.
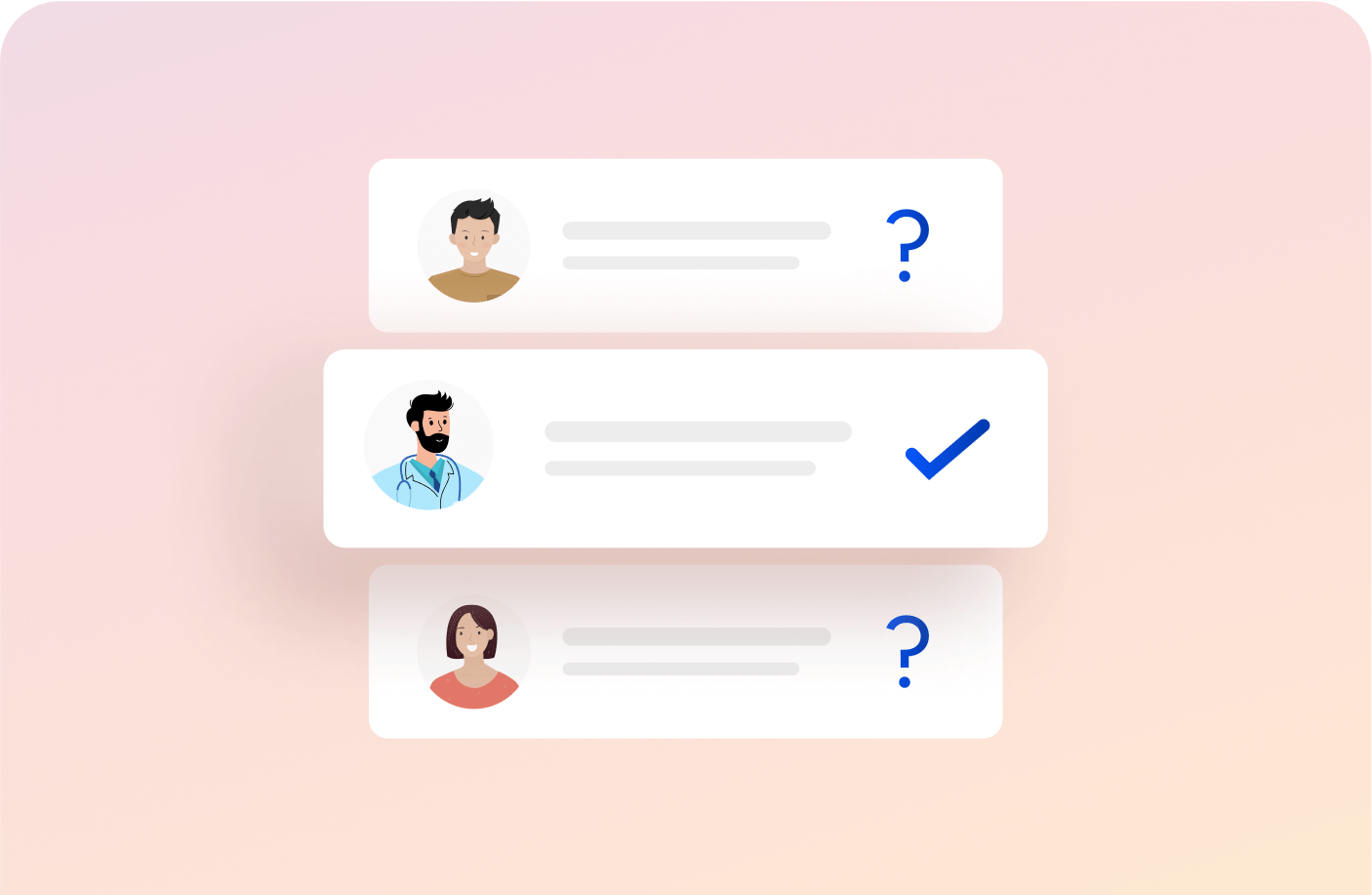
Detailed Doubt Clearance
Attend live doubt-solving sessions and clarify concepts from our dedicated faculty.
Linker Videos
Linker videos bridge Basic Sciences with clinical applications, showcasing clinical case studies for AETCOM integration in the CBME curriculum.
The Course Contains
- CBME mapped and integrated curriculum
- 1000+ learning modules
- Lecture videos with notes
- Comprehensive pedagogy (Overview, Learn, Resource Centre, and Test)
- Glossary for quick search
- CYU with 50+ flashcards
- Customization of playlists for quick reference
- 1000+ interactive content with gamified assessments
FAQ
Where can I access the content?
Can I share my subscription?
No, subscriptions cannot be shared since study plans and guides are uniquely tailored to each student's needs. Also, videos cannot be played on 2 devices with same login credentials simultaenously.
Can I download the content and watch it offline?
Yes! You can download up to 5 modules at a time. When you download more than 5 modules, earlier downloaded videos will be made available online.
Are there live classes available?
Most of the video classes are recorded so you can learn at your own pace.
Is there a free trial available?
Are there notes available in the MedAce app?
Yes, MedAce provides in-app digital notes that can be conveniently downloaded within the app itself. You can access and refer to these digital notes while using the app for a seamless learning experience.
Is it possible to cancel my purchase and receive a refund?
Certainly, it is possible to cancel your purchase. However, please note that no refunds are given. After you cancel, you will still have access to the service until the end of your billing period.
Want to know more?
Fill out the form below, and our team of experts will get in touch to promptly solve all your doubts.